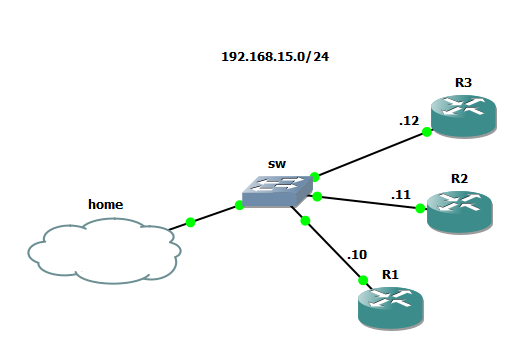
The last few examples of using netmiko hasn’t really been very scalable as the devices was provided as a list directly in the code. In this example I thought we could try out and use YAML for an inventory-file instead.
My very small network could look like this (but preferably you would use getpass() instead of writing it directly in your script):
inventory.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
all:
vars:
username: joco02
password: cisco
sites:
- name: gns3
hosts:
- hostname: R1
host: 192.168.15.10
device_type: cisco_ios
- hostname: R2
host: 192.168.15.11
device_type: cisco_ios
- hostname: R3
host: 192.168.15.12
device_type: cisco_ios
We then import “yaml” in our python-script, read the file and we will have a very nice dictionary to work with! If we wanted to we could divide our topology in different sites and decide for ourselves on which devices we want to run the script instead of all like I do here.
yaml_ouput.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
import yaml
def read_yaml(path="inventory.yml"):
with open(path) as f:
yaml_content = yaml.safe_load(f.read())
return yaml_content
def main():
parsed_yaml = read_yaml()
print(parsed_yaml)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Output:
1
2
$ python login.py
{'all': {'vars': {'username': 'joco02', 'password': 'cisco'}, 'sites': [{'name': 'gns3', 'hosts': [{'hostname': 'R1', 'host': '192.168.15.10', 'device_type': 'cisco_ios'}, {'hostname': 'R2', 'host': '192.168.15.11', 'device_type': 'cisco_ios'}, {'hostname': 'R3', 'host': '192.168.15.12', 'device_type': 'cisco_ios'}]}]}}
So let’s rework our previous script so we only use your yaml-file as input to netmiko. It’s a little tricky at first if your as me, not super confident with using dictionaries in python.
We create an empty dict for every device and insert the login credentials, device_type and ip-address from the parsed_yaml dict which we then send over to netmiko with the standard “ConnectHandler(**device)”.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
from datetime import datetime
from copy import deepcopy
import yaml
SH_COMMANDS = [
"show ip route | beg Gate", "show ip interface brief | excl admin"
]
def read_yaml(path="inventory.yml"):
with open(path) as f:
yaml_content = yaml.safe_load(f.read())
return yaml_content
def get_connection_parameters(parsed_yaml):
parsed_yaml = deepcopy(parsed_yaml)
login_credentials = parsed_yaml["all"]["vars"]
for site_dict in parsed_yaml["all"]["sites"]:
for host in site_dict["hosts"]:
host_dict = {}
host_dict.update(login_credentials)
host_dict.update(host)
yield host_dict
def show_commands(devices, commands):
for device in devices:
start_time = datetime.now()
hostname = device.pop("hostname")
connection = ConnectHandler(**device)
device_result = ["{0} {1} {0}".format("=" * 15, hostname)]
for command in commands:
command_result = connection.send_command(command)
device_result.append("{0} {1} {0}".format("=" * 10, command))
device_result.append(command_result)
device_result_string = "\n\n".join(device_result)
connection.disconnect()
device_result_string += "\nElapsed time: " + str(datetime.now() - start_time)
yield device_result_string
def main():
parsed_yaml = read_yaml()
print(parsed_yaml)
connection_parameters = get_connection_parameters(parsed_yaml, site_name=SITE_NAME)
for device_result in show_commands(connection_parameters, SH_COMMANDS):
print(device_result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
$ python login.py
=============== R1 ===============
========== show ip route | beg Gate ==========
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.15.254 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.15.254
192.168.15.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.15.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
L 192.168.15.10/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
========== show ip interface brief | excl admin ==========
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0/0 192.168.15.10 YES manual up up
Elapsed time: 0:00:05.841709
=============== R2 ===============
========== show ip route | beg Gate ==========
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.15.254 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.15.254
192.168.15.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.15.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
L 192.168.15.11/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
========== show ip interface brief | excl admin ==========
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0/0 192.168.15.11 YES manual up up
Elapsed time: 0:00:05.805187
=============== R3 ===============
========== show ip route | beg Gate ==========
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.15.254 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.15.254
192.168.15.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.15.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
L 192.168.15.12/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
========== show ip interface brief | excl admin ==========
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0/0 192.168.15.12 YES manual up up